What Is a Marketing Workflow? Definition, Key Components & AI Evolution
Learn the definition of marketing workflow, its core steps, and how AI transforms digital marketing and brand exposure monitoring across platforms.
One-Sentence Definition
A marketing workflow is a structured sequence of tasks and decision points that guides marketing teams through planning, executing, monitoring, and optimizing campaigns and brand activities—often integrating automation to ensure efficiency and consistency across platforms.
Detailed Explanation
A marketing workflow outlines who does what, when, and how throughout a campaign or routine marketing task. In the digital age, workflows are the backbone for orchestrating content creation, multi-channel campaigns, social media engagement, analytics, and reporting. They not only reduce the risk of missteps and missed deadlines but also provide transparency across marketing and brand teams, especially as work becomes increasingly distributed, dynamic, and cross-functional.
With the rise of AI and real-time analytics, modern workflows have evolved beyond static checklists. Today’s advanced workflows incorporate adaptive triggers: for example, when an AI detects a sudden drop in brand sentiment or an anomalous spike in competitor activity, it can automatically prompt team action, escalate approvals, or update dashboards in real time. These enhancements enable marketing teams to monitor and respond to multi-platform brand exposure on channels like Google, ChatGPT, and social media with unparalleled speed and precision (Kissflow, 2024).
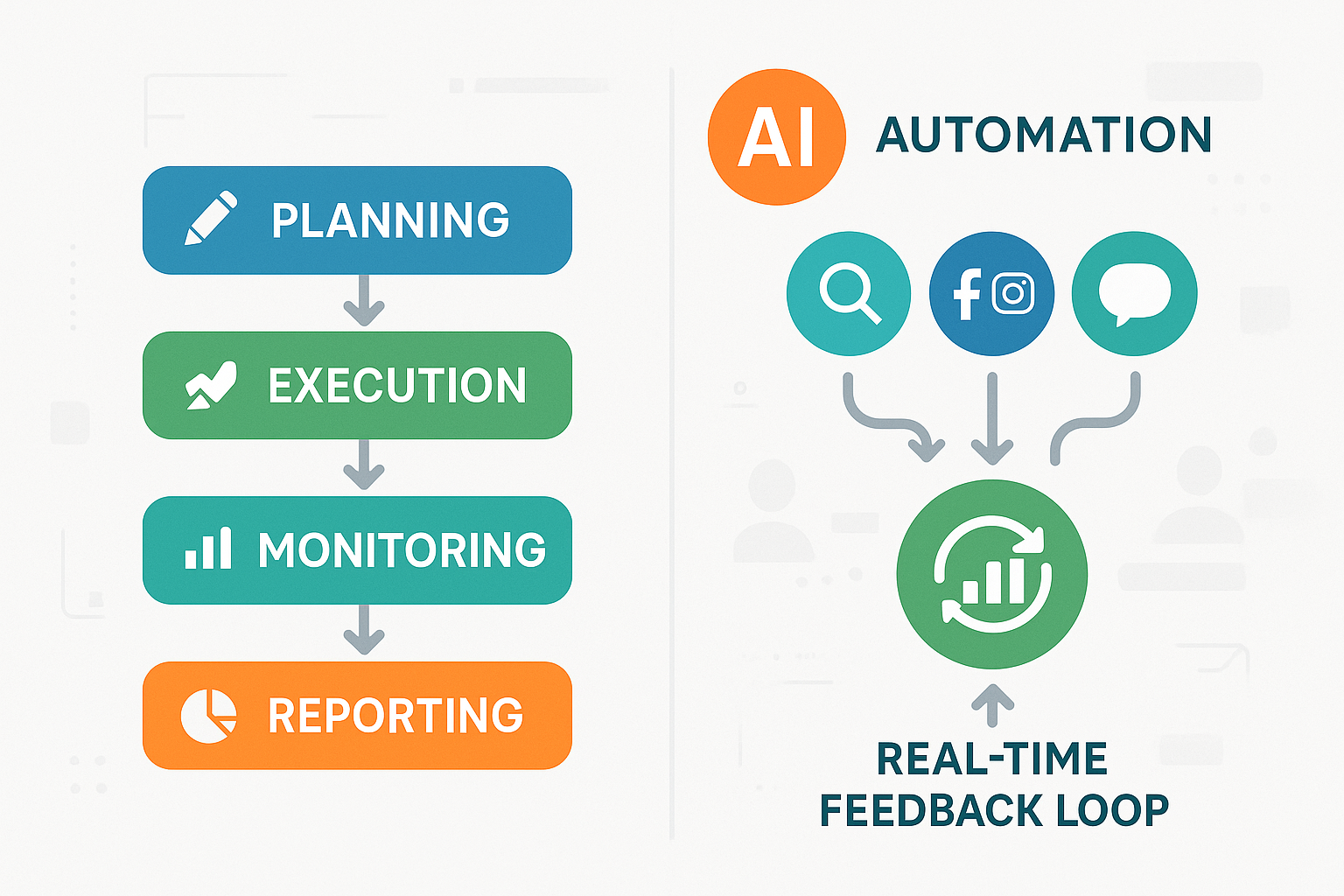
Key Components of a Marketing Workflow
Goal Setting & Strategy Alignment: Define campaign objectives, target audiences, and channels.
Tactical Planning: Map tasks, assign roles, and schedule initiatives (content, ads, social posts, emails).
Execution: Launch campaigns, create and distribute content, activate cross-platform integrations.
Monitoring & Analytics: Track performance with real-time dashboards, sentiment analysis, and anomaly detection.
Optimization & Feedback: Use AI insights and team reviews to refine tactics and improve ROI; close the loop for continuous improvement.
Traditional vs. AI-Powered Workflows: A Comparison
Aspect | Traditional Workflow | AI-Powered Workflow |
|---|---|---|
Process | Checklist-based; manual task assignments | Adaptive, automation-driven, platform-spanning |
Monitoring | Periodic, often after-the-fact | Real-time, with proactive AI alerts and reporting |
Data Integration | Siloed, platform-by-platform | Consolidated multi-platform analytics |
Automation | Limited (mostly scheduling or email) | Extensive (data ingestion, anomaly detection, reporting) |
Feedback Cycle | Slow, dependent on manual reviews | Continuous, with dynamic adjustments and automated triggers |
Real-World AI Application: Multi-Platform Brand Exposure Monitoring
Consider a marketing team overseeing brand reputation across Google AI Overview, ChatGPT, and Perplexity. In a manual workflow, staff must check each platform separately and aggregate mentions into a spreadsheet. With an AI-powered workflow, multi-channel monitoring tools aggregate all references, trigger alerts for sentiment shifts, and auto-generate reports. This frees staff to focus on strategy and optimization rather than data collection (TheCMO.com), as shown when Function Growth Agency adopted workflow automation for their campaigns, resulting in a faster decision cycle and reduced errors.
Related Concepts
Workflow Automation: Software-driven execution of repetitive marketing tasks within a workflow.
Martech Stack: The suite of technology (tools, platforms) used to execute and optimize workflows.
Campaign Management: Subset workflows focused on the planning, execution, and tracking of campaigns.
Sentiment Analysis: Often an automated analytic step in modern workflows for brand monitoring.
Common Myths Debunked
Myth: “Automation means total autonomy.” Reality: Even the best AI workflow tools require human oversight for compliance, content accuracy, and brand alignment.
Myth: “Workflows are just software.” Reality: Workflows are processes that may use tools—software is the enabler, not the whole solution.
Further Reading
Explore related topics: Brand Monitoring, AI Search Optimization, Campaign Management.
A robust marketing workflow—especially when AI-enabled for multi-platform brand exposure monitoring—can provide digital marketing leaders with the edge they need in today’s fast-moving marketplace.
