What is KPI? Key Performance Indicator Definition & Digital Marketing Uses
Learn what a Key Performance Indicator (KPI) is, how KPIs drive digital marketing, key components, pitfalls, and AI-powered KPI examples.
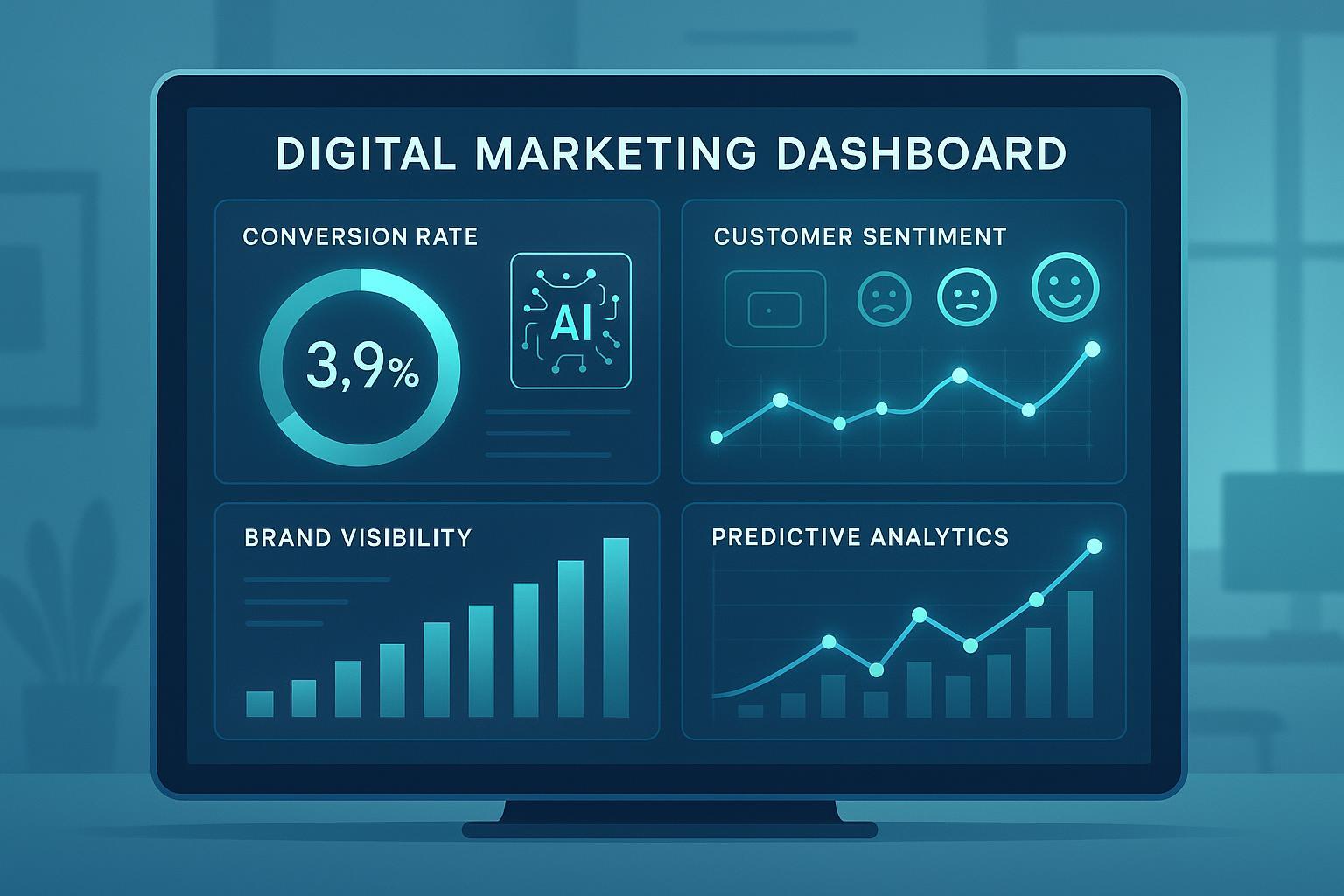
A Key Performance Indicator (KPI) is a quantifiable metric used to gauge how effectively an organization or campaign achieves its defined objectives, particularly within digital marketing and AI-enhanced brand management.
Detailed Explanation
KPIs are the cornerstone of performance measurement in business and marketing. They translate complex objectives—like growing brand awareness, increasing customer engagement, or maximizing return on investment—into concrete, measurable signals for success or improvement. In digital marketing, KPIs help professionals cut through data overload, focus on what truly matters, and adjust tactics in real-time or over the course of a campaign.
KPIs come in all shapes and sizes, but effective ones share specific traits:
- Specific and aligned: Directly tied to core business goals (e.g., boost leads, grow social reach).
- Measurable and actionable: Use clearly defined data sources and metrics.
- Relevant and timely: Provide current performance snapshots and can be acted upon immediately.
The practical framework for KPI selection is the SMART model: Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound (Improvado). Leading organizations also use cascading KPIs (from executives to operational teams) and regular benchmarking to ensure relevance and competitiveness.
Key Components of KPIs
- Objective alignment: KPIs must be linked to specific, strategic business aims.
- Data quality: The metrics must be based on reliable, up-to-date data sources such as marketing platforms, web analytics, or social listening tools.
- Actionability: The information provided should drive informed decisions and clear next steps for marketing or branding teams.
- Context and benchmarking: Effective KPIs are tracked over time and compared against industry standards or competitors.
Real-World Application: Classic vs. AI-Driven KPIs
Traditional KPIs in digital marketing include:
- Conversion Rate (percentage of visitors completing a desired action)
- Cost Per Acquisition (CPA)
- Website Traffic
- Click-Through Rate (CTR)
- Brand Awareness (reach, impressions)
AI-powered and modern KPIs expand these capabilities:
- Sentiment Analysis KPIs: Using natural language processing to score the emotional tone of brand mentions across social and AI-generated content (MIT Sloan).
- Predictive Analytics KPIs: Leveraging machine learning algorithms to forecast campaign performance, identify churn risks, or optimize budget allocation in real time.
- Engagement Quality Prediction: AI models interpret not just how many users interacted, but how significant or positive those engagements were.
Scenario: A brand launching a digital campaign might set classic KPIs (conversions, CPA) alongside modern KPIs (real-time brand sentiment, AI-predicted engagement changes). Dashboards integrating both types enable continuous adjustment and smarter strategy refinement.
Common Pitfalls and Best Practices
- Avoid vanity metrics (like raw follower counts) that do not link back to business objectives.
- Limit KPIs to a manageable set—too many indicators dilute focus and lead to confusion.
- Regularly revisit KPI relevance as campaigns or brand strategy evolve.
Related Concepts
- Metric: Any measurement, not always strategic or goal-oriented.
- Objective: The desired end goal, which KPIs are designed to measure progress toward.
- ROI (Return on Investment): A core KPI assessing profitability and efficiency (Investopedia).
- CPA (Cost Per Acquisition): Measures the cost of securing a customer.
- Conversion Rate: Tracks success at turning prospects into customers (Landingi).
- Brand Awareness and Sentiment Analysis: Modern KPIs offer deeper insight into not just how many people see your brand, but how they feel about it.
For deeper information: KPI Basics – KPI.org | Wrike Marketing Guide to KPIs | MIT Sloan: AI and KPI Integration
