How to Get Content Cited in AI-Generated Search Answers: Step-by-Step Guide
Learn a step-by-step strategy to optimize content for citations in Google AI Overviews, Bing Copilot, Perplexity, and ChatGPT—beyond traditional rankings.
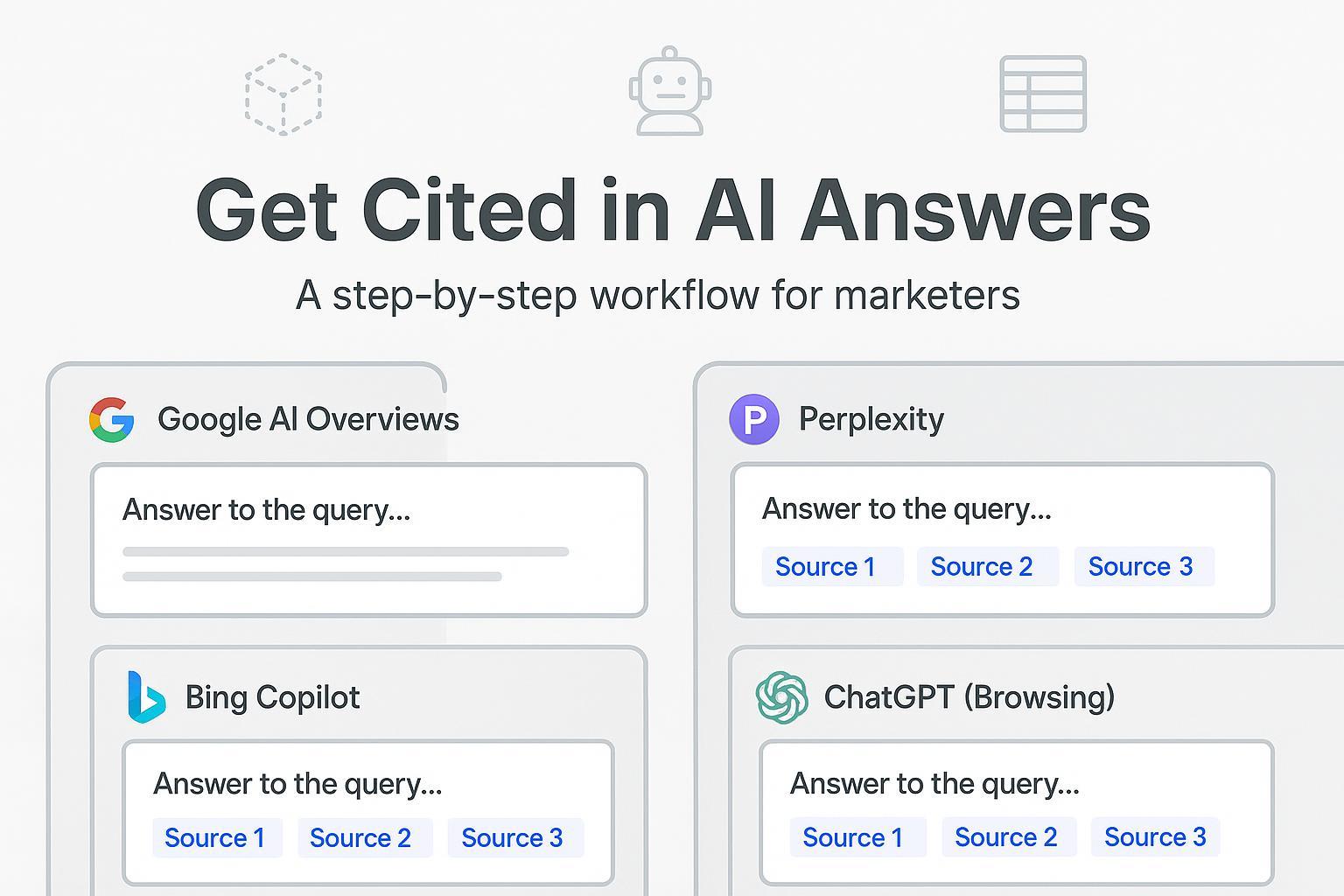
If your organic playbook is built around “rank top 3,” you’re missing where user attention is shifting: AI-generated answers. This tutorial walks you through a practical workflow to make your pages extractable, trustworthy, and measurable so they’re more likely to be cited by Google AI Overviews, Bing Copilot, Perplexity, and ChatGPT with browsing.
- Difficulty: Intermediate (comfortable with basic SEO and CMS edits)
- Time: 1–2 days to implement for a first batch of pages, plus ongoing 30/60/90-day reviews
- Prerequisites: Access to your CMS, Google Search Console, Bing Webmaster Tools, robots.txt, and basic JSON-LD editing/validation
Why this matters: In 2025, AI answers frequently include source links but selection patterns differ by engine. Google’s AI features explain that summaries are grounded in core ranking systems and draw from structured data and indexed content (Google Search Central: AI features and your website, 2025). Bing Copilot notes it grounds answers in top web results with visible "Learn more" references (Microsoft: Copilot in Bing – our approach to citations, 2025). Independent studies also show engines like Perplexity cite a mix of authoritative sites and UGC sources such as Reddit (Amsive/Profound platform citation patterns, 2025).
Step 1: Baseline your AI citation status and prioritize queries
Start with a quick audit to see where you already appear and where gaps exist.
- List 25–50 high-value queries (commercial, how-to, and informational) that matter to your business.
- For each query, check the four engines:
- Google: Search and open the AI Overview/AI mode if available; note whether your domain appears in the citations at the end of the summary.
- Bing Copilot: Ask the query; look for the "Learn more" links and check if your page is among them.
- Perplexity: Enter the query; scan inline citations; note whether UGC dominates the sources.
- ChatGPT (browsing enabled): Ask the query; see if your page is visited and cited in the final answer.
- Track results in a spreadsheet with columns: Engine, Query, Cited? URL, Link present? Snippet accuracy, Sentiment (positive/neutral/negative), Notes, Next action.
Tip: Expect different citation volume by engine. Perplexity typically shows many citations; Copilot often shows fewer and leans conservative in source choice, as industry analyses observed in 2025 (Amsive/Profound). That’s normal—your tactics will adapt.
Step 2: Engineer answer-first pages for extractability
Most AI engines perform better with pages that lead with a concise, citable answer and then expand.
- Create a visible "Key answer" section at the top (2–3 plain-language sentences). Keep it unambiguous and source-worthy.
- Follow with structured depth:
- Use H2/H3s to separate subtopics
- Add bullets for lists of steps or criteria
- Include simple tables for comparisons or stats
- Add an FAQ section answering 3–6 tightly scoped questions
- Keep HTML clean. Avoid hiding key text behind heavy scripts or tabs that only load on interaction. This aids machine readability.
Note: Google confirms AI features draw from structured data and indexed content, and clear structure helps engines extract reliable snippets (Google Search Central, 2025).
Common mistake to avoid: Writing a long intro before the answer. Lead with the answer or definition, then elaborate.
Step 3: Add structured data (schema) and validate it
Structured data clarifies what your page contains and who stands behind it.
- Implement JSON-LD for Article + Person (author) + Organization (publisher). Add FAQPage or HowTo schema when eligible (FAQ must match visible Q&A; HowTo only for real step-by-step processes).
- Validate using Google’s Rich Results Test and Schema.org’s validator.
- Ensure your schema mirrors visible content. Don’t mark up hidden or non-existent text.
Example JSON-LD (condensed):
{
"@context": "https://schema.org",
"@type": "Article",
"headline": "How to be cited in AI-generated answers",
"datePublished": "2025-10-04",
"author": {
"@type": "Person",
"name": "Your Author",
"jobTitle": "SEO Strategist",
"sameAs": ["https://www.linkedin.com/in/yourauthor"]
},
"publisher": {
"@type": "Organization",
"name": "Your Brand",
"logo": {
"@type": "ImageObject",
"url": "https://example.com/logo.png"
},
"sameAs": ["https://twitter.com/yourbrand", "https://www.crunchbase.com/organization/your-brand"]
}
}
- FAQPage guidance: See Google’s documentation for required properties and on-page parity in the FAQPage structured data guide (updated 2025).
- QAPage is only for pages with user-submitted answers, per the QAPage structured data guidelines.
- General intro and validator links are in Google’s structured data overview and the Schema Markup Validator.
Troubleshooting: If validators show errors, check required properties (e.g., acceptedAnswer for FAQPage) and ensure values match your visible content.
Step 4: Strengthen entity clarity and E-E-A-T signals
Make it easy for engines to understand who wrote the page and why it’s trustworthy.
- Add detailed author bios with credentials and relevant experience; link them from each article.
- Use Person and Organization schema with sameAs links to authoritative profiles (LinkedIn, Crunchbase, official social pages).
- Maintain transparent About and Contact pages; avoid fake or inflated credentials.
According to Google’s guidance on AI and Search quality, aligning with E-E-A-T principles and clear authorship helps the system assess your content’s reliability (Google’s Search and AI content guidance, maintained through 2025). Search Engine Land’s 2025 guide also synthesizes how E-E-A-T supports SEO programs.
Step 5: Ensure crawler access and technical hygiene
If engines can’t fetch or render your content, they can’t cite it.
- Confirm crawlability and indexability:
- No unintended noindex tags
- Correct canonical tags
- Important resources (CSS/JS/images) aren’t blocked
- Use Google Search Console’s URL Inspection and Coverage reports to verify indexing. If your page is JavaScript-heavy, consider server-side rendering or pre-rendering to ensure the full content is HTML-accessible.
- Configure robots.txt with explicit allowances for legitimate bots you want to access:
# Allow major bots
User-agent: Googlebot
Allow: /
User-agent: Bingbot
Allow: /
# GPTBot (ChatGPT)
User-agent: GPTBot
Allow: /
- Google’s crawling/indexing hub explains rendering and JS SEO basics, including when SSR or pre-rendering can help (Google crawling and indexing documentation, 2025; JavaScript SEO basics, 2025).
- Perplexity crawler behavior is disputed. Cloudflare’s 2025 report alleges stealth crawls that ignore robots.txt, while Perplexity contests aspects of these claims. Decide a policy (allow/deny) and monitor logs; see the discussion in the Cloudflare blog on Perplexity crawlers.
Note: Blocking all AI bots reduces the likelihood of being cited. If you aim for AI visibility, allow compliant bots and ensure content is easily retrievable.
Step 6: Publish, request recrawl, and stabilize URLs
- Publish or update your page; include a clear “Updated on” date and, if relevant, a changelog of what changed.
- Update your XML sitemap and ensure lastmod is accurate.
- In Google Search Console, use URL Inspection → Request indexing for materially updated pages.
- Avoid changing URLs; stable URLs help consolidating signals over time.
Step 7: Verify citations and measure by engine
Within 2–4 weeks, recheck your target queries and document progress.
- Google AI Overviews: Scan the sources listed in the AI summary and record whether your URL appears; note accuracy of the snippet.
- Bing Copilot: Check the "Learn more" references and whether your page is included.
- Perplexity: Review inline citations; note whether your facts are used, especially tables and definitions.
- ChatGPT browsing: Confirm whether GPTBot fetched your page (server logs) and whether the final answer includes your link.
For ongoing tracking, simple spreadsheets work, but third-party trackers can add efficiency. For background on trackers and methodology differences, see the 2025 roundup of AIO tracking tools by SitePoint.
Step 8: Distribute and earn authority from credible ecosystems
Engines that weigh authority and UGC benefit from a mix of expert coverage and community signals.
- Publish original data and methods; present clean tables and short summaries.
- Pitch credible outlets and niche industry publications; contribute expert quotes.
- Participate ethically in communities (Reddit, Stack Exchange, specialized forums). Avoid astroturfing.
Analyses in 2025 observed that engines like Perplexity frequently surface UGC sources alongside authoritative sites (Amsive/Profound), so community credibility can influence visibility.
Step 9: Refresh cadence (30/60/90 days)
- 30 days: Fix schema issues, improve answer-first clarity, add a short FAQ.
- 60 days: Add or update original data, tables, or examples; adjust robots/access if logs show problems.
- 90 days: Expand topical coverage (supporting articles), strengthen author/organization entities, and re-pitch new findings.
Practical example: Measuring AI citations and iterating
Disclosure: Geneo is our product.
Here’s a neutral, replicable way to operationalize measurement and iteration.
- Set up a query list and monitor whether your site is cited across major AI engines. A platform like Geneo supports tracking AI visibility across Google AI Overviews, Perplexity, and ChatGPT, including sentiment and historical query records.
- Use the baseline spreadsheet you created in Step 1 as your source of truth. When Geneo or your manual checks show a gap (e.g., Perplexity cites Reddit and rivals but not you), prioritize improving extractability: tighten your top-of-page answer, add a comparison table, and ensure FAQPage markup matches visible content.
- When you earn citations, note whether engines link back (Google AI Overviews and Perplexity typically do; Copilot varies by UI) and whether the snippet reflects your facts accurately. Refresh content if answers are misinterpreted.
Troubleshooting quick wins
- Schema errors: Revalidate JSON-LD; ensure on-page parity; fix required properties (e.g., acceptedAnswer for FAQPage).
- Indexing gaps: Check robots/noindex/canonical; request indexing; link the page internally from already-indexed pages.
- Not cited after 60–90 days: Improve extractability and originality (add unique data, tables); build external authority with expert coverage; align with engine-specific patterns (e.g., Perplexity’s UGC mix, Copilot’s alignment with Bing results).
Next steps
- Pick 5–10 priority queries and run Steps 1–3 today.
- Ship improvements, request indexing, and set calendar reminders for 30/60/90-day reviews.
- If you need an ongoing, consolidated view of AI citations and sentiment across engines, you can explore the broader GEO insights on the Geneo blog.
References and further reading
- Google’s overview of how AI features interact with websites (May 2025): Google Search Central – AI features and your website
- Structured data docs (FAQPage, QAPage, intro) and validator: FAQPage guide · QAPage guidelines · Intro to structured data · Schema Markup Validator
- Crawling/indexing and JavaScript SEO: Google crawling and indexing hub · JavaScript SEO basics
- Bing Copilot’s citation approach: Microsoft – Copilot in Bing citations
- Platform citation patterns: Amsive/Profound – AI platform citation patterns
- Crawler controversy discussion: Cloudflare – Perplexity stealth crawlers
