Cross-lingual Generative Engine Optimization Best Practices (2025)
Discover 2025's best practices for cross-lingual generative engine optimization. Practical workflows for brand managers, digital marketers, and SEO pros—including multilingual AI search, actionable GEO tactics, and Geneo-powered monitoring.
Generative search is now the front door for discovery in many markets. If your brand isn’t cited, summarized, or recommended in a user’s language, you’re invisible—even if your traditional SEO is strong. This playbook distills what has worked across multilingual launches and remediation projects in 2024–2025, with a focus on practical steps you can run this quarter.
Key idea: Winning the generative layer requires language-first information architecture, evidence-dense content that’s easy to cite, impeccable international SEO hygiene (hreflang, structured data), and a tight monitor–optimize cycle across platforms and languages.
—
1) Why cross‑lingual GEO is different (and harder)
- Generative engines compress and translate. A French prompt may surface English sources, translate them, and attribute selectively. Your job is to make your localized page the easiest high‑trust source to summarize and cite.
- Platform behavior varies:
- Google’s AI Overviews selects and cites sources drawn from the open web; evidence clarity and page accessibility are prerequisites, per Google’s 2025 guidance on succeeding in AI-led search as reflected in the official Search Central blog’s focus on helpful, reliable content and technical accessibility (see Google’s evolving AI search guidance in 2025).
- Perplexity privileges concise, well‑structured facts with clear citations. Short, answer‑ready sections and explicit metadata improve inclusion, consistent with its product behavior and help materials emphasizing transparent source citation.
- ChatGPT with browsing uses a crawler-friendly path and tends to cite canonical, authoritative pages when answers depend on live content.
- Cross‑language routing is fragile. Without correct hreflang and localized versions, engines may cite your English page into Spanish answers. Google’s internationalization docs explicitly require reciprocal hreflang between localized variants to serve the right version, documented in the Search Central guide to localized versions: Google Search Central – localized versions (hreflang).
Practical implication: Treat each language as a first‑class surface. Make it verifiably local, technically unambiguous, and citation‑ready.
—
2) Build the multilingual foundation the engines can trust
These are baseline requirements before content refreshes.
- Map your language–region matrix
- Decide languages and regional variants (e.g., es-ES vs es-MX). Keep a single, clean URL per locale with a stable pattern (e.g., /es-es/, /es-mx/).
- Publish an index of all locales and maintain parity of core pages.
- Implement hreflang correctly
- Use reciprocal hreflang on every localized page, include x‑default for a global fallback, and reflect the full set in XML sitemaps. Follow Google’s localized versions (hreflang) documentation.
- Common pitfall: orphaned locales or partial reciprocity causing English pages to be cited in non‑English answers.
- Declare language in structured data and HTML
- Set lang attributes and use Schema.org’s inLanguage where relevant (e.g., on CreativeWork, Article). See Schema.org – inLanguage.
- Keep author and organization markup consistent; centralize brand identity in Organization schema.
- Reference Google’s structured data guidance hub for implementation specifics: Google – Structured data (Search Central).
- Make pages crawler- and citation‑friendly
- Avoid paywalls or heavy JS blocking for key proof pages; ensure clean, linkable anchors for claims, definitions, and stats.
- Provide stable permalinks for glossary and methodology sections.
—
3) Design content that answer engines love to cite
What I’ve seen consistently improve inclusion across languages:
- Evidence packaging over prose. Lead with the claim, then support it. Use short paragraphs, bullets, and callouts that engines can lift.
- Localized definitions and glossaries. Add market‑specific terminology; engines routinely extract and translate these.
- Q&A blocks for common prompts. Place succinct answers (40–120 words) with one or two authoritative references.
- Numbers with provenance. When quoting a stat, include year and publisher next to it and link the exact artifact page via a descriptive anchor. For example, when supporting multilingual fundamentals, cite the Google Search Central – localized versions (2025) page.
- Author and brand signals on every locale. Clear bylines, org markup, and about pages build trust that travels across languages.
—
4) Platform‑specific tactics (2025)
A. Google AI Overviews
- Optimize for factual extractability. Use tight sections with headers like “Cost,” “Eligibility,” “Steps,” and “Proof.”
- Strengthen E‑E‑A‑T signals. Prominent author creds, organization schema, and method notes help selection in AI Overviews per Google’s Search Central guidance on helpful, reliable content in 2025. Pair with structured data where applicable: Google – Structured data overview.
- Ensure correct locale is the easiest to cite. Hreflang fidelity is non‑negotiable: Google – localized versions (hreflang).
B. Perplexity
- Embrace answer‑first blocks. Start sections with a one‑sentence answer, follow with 2–3 bullets and 1–2 links using descriptive anchors to primary documents.
- Maintain concise, high‑signal pages for “how/what” queries in each language. Perplexity tends to surface dense, well‑sourced content.
C. ChatGPT/Browsing and similar assistants
- Make live content accessible and clearly authored. Browsers prefer canonical, stable pages with explicit authorship and updated timestamps.
- Provide language‑native proof assets (PDF summaries, data tables) when possible; ensure they are crawlable and tagged with inLanguage.
—
5) Monitoring, diagnostics, and iteration with Geneo
In practice, multilingual GEO is won through tight feedback loops. Here’s a field‑tested workflow using Geneo.
Step 1: Establish baselines per language and platform
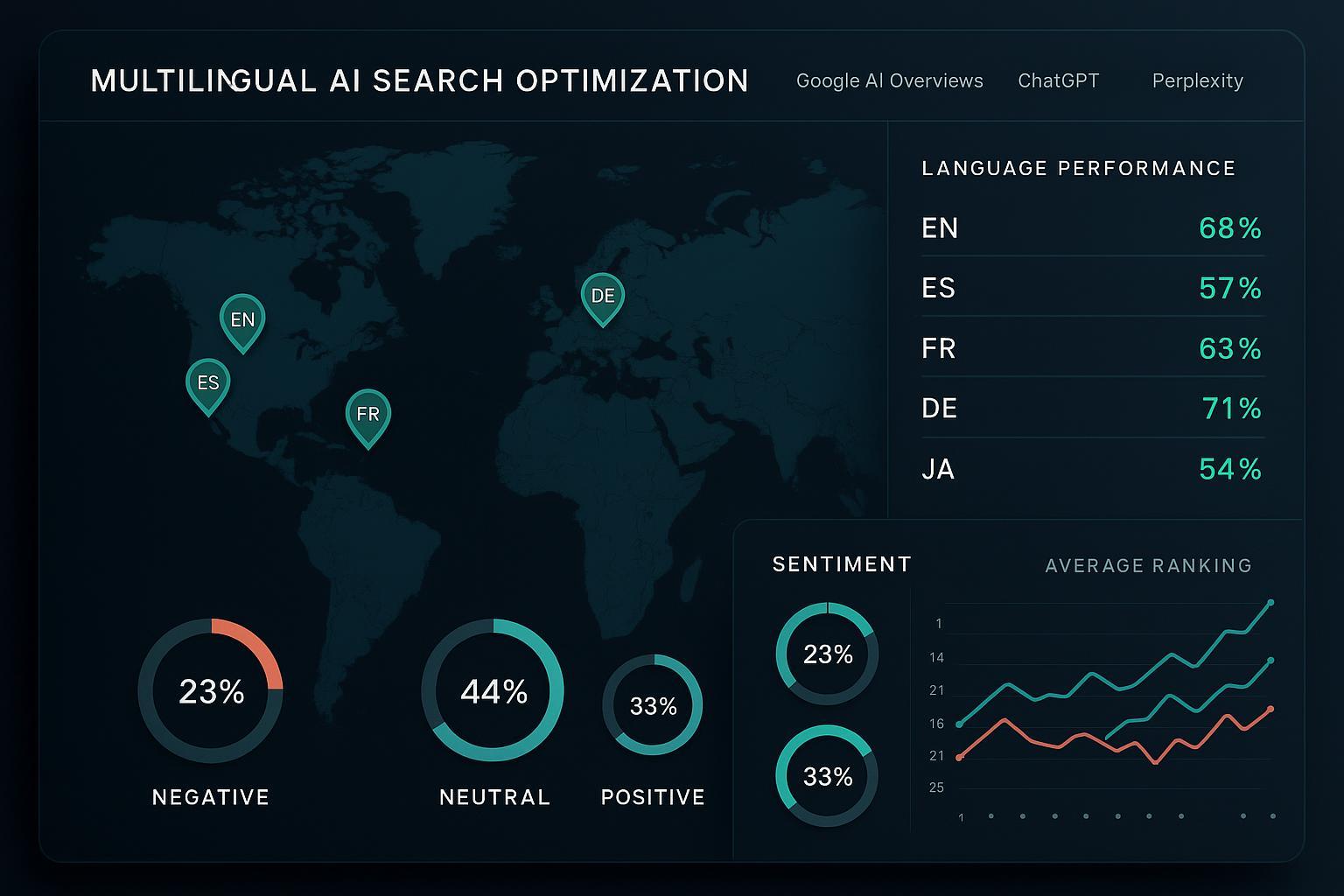
- In Geneo, create a workspace per brand and add target locales (e.g., EN-US, ES-MX, FR-FR, DE-DE, JA-JP).
- Track exposure and citations in ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews for priority queries (brand, category, and competitor prompts). Geneo’s real‑time cross‑platform monitoring highlights where your brand is missing or misattributed.
Step 2: Sentiment and answer-quality audits
- Use Geneo’s multilingual sentiment analysis to flag negative or misleading summaries. Prioritize languages where sentiment dips below neutral and drill into the cited sources.
- Identify hallucination vectors (e.g., outdated press releases, mislocalized FAQs) and queue content fixes.
Step 3: Iterate content and structure
- For each weak locale, update Q&A blocks, add localized glossaries, strengthen evidence callouts, and ensure hreflang reciprocity.
- Geneo’s historical query tracking lets you A/B test snippet formats (e.g., 80‑word vs 120‑word answers) and compare inclusion deltas week over week.
Step 4: Expand surface area strategically
- Use Geneo’s content optimization suggestions to identify gaps by language (e.g., missing “eligibility” sections in Spanish pages that rivals have). Ship small, iterative fixes, then monitor.
Step 5: Report and govern
- Build a monthly multilingual GEO report: citation share by platform, sentiment by language, inclusion rate of target pages, and change log of interventions. Geneo’s multi‑brand support simplifies executive‑level rollups across markets.
—
6) Measurement: the KPI ladder for GEO
Track leading indicators (fast feedback) and lagging indicators (business impact) per language.
Leading indicators (weekly):
- Inclusion rate in AI Overviews/answers for target prompts by locale
- Citation share vs. competitors within answers
- Sentiment score of generated summaries
- Number of answer‑ready blocks deployed per locale
Lagging indicators (monthly/quarterly):
- Assisted traffic from AI answer widgets and related SERP features
- Branded and category query lift by locale
- Conversion and revenue influenced by GEO pages
Governance metric:
- Hreflang integrity score (reciprocity and coverage)
- Schema completeness (author, organization, inLanguage)
—
7) Operating model: people, process, and SLAs
- Roles: Pair a localization PM with an international SEO lead and a content strategist per region. Give engineering a recurring slot for hreflang and schema fixes.
- SLAs: 2–3 day turnaround for factual corrections; 2‑week cadence for structured content improvements; monthly hreflang audits.
- Localization QA: Linguist review for terminology, measurement units, and examples; ensure examples are region‑true (e.g., pricing, regulations).
- Brand safety: Monitor negative sentiment; where misstatements propagate, publish a concise “Corrections” note in the local language and strengthen citations on the corrective page.
—
8) Common failure patterns and how to fix them
- The English page keeps getting cited in other languages
- Fix: Implement reciprocal hreflang, add x‑default, ensure localized page has equal or better evidence packaging. Validate using Google’s guidance for localized versions (hreflang).
- Engines summarize outdated information
- Fix: Update timestamps prominently, add a “Last reviewed” block, and link to underlying primary sources with year and publisher in the anchor. Keep structured data current per Google’s structured data documentation.
- Your localized content is too literal
- Fix: Localize for cultural context—examples, regulations, unit systems—and add locale‑specific FAQs. Tag pages with inLanguage and ensure the local version is the strongest source: Schema.org – inLanguage.
- No visibility in Perplexity despite good SEO
- Fix: Tighten answers and proof. Lead with the conclusion, follow with 2–3 bullets, and link canonical, primary sources using descriptive anchors.
—
9) A pragmatic 90‑day rollout plan
Days 1–15: Baseline and hygiene
- Inventory locales, map URL patterns, and audit hreflang and inLanguage usage.
- Stand up Geneo with target prompts per locale; capture baseline inclusion, citations, and sentiment across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews.
Days 16–45: Content restructuring
- Deploy Q&A blocks, localized glossaries, and evidence callouts on top 20 pages per priority locale.
- Implement schema updates (Organization, Article, author) and verify technical accessibility.
Days 46–75: Iteration and A/B testing
- Use Geneo’s historical tracking to test answer lengths, headings, and citation placement. Fix locales with negative sentiment or low inclusion first.
Days 76–90: Scale and governance
- Create a repeatable monthly GEO report and playbook; schedule quarterly hreflang and schema audits. Expand to secondary locales.
—
References and technical resources
- Google’s canonical documentation on internationalization via hreflang: Google Search Central – localized versions (hreflang)
- Language declaration in structured data: Schema.org – inLanguage
- Structured data implementation hub: Google – Structured data (Search Central)
—
How Geneo fits your GEO program
Geneo monitors your brand’s visibility, citations, and sentiment across ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google AI Overviews in real time—then turns those insights into concrete content optimization suggestions per language. For teams running multi‑market programs, Geneo’s multi‑brand workspaces, historical query tracking, and multilingual sentiment analysis close the loop between monitoring and action.
Try Geneo to operationalize the workflows in this guide: https://geneo.app





